
The Business Value of Observability in IT Systems
IT systems are no longer just support functions today, but they are the business. From customer onboarding and payments to supply chain management and analytics, every important business outcome depends on complex, distributed technology ecosystems.
Yet, many organizations still monitor IT performance in silos, tracking infrastructure uptime, application metrics, or logs independently, without truly understanding how technology behavior impacts business results.
This is where Business Observability becomes a strategic differentiator.
Experts at PCPL believe observability is a business intelligence capability that bridges the gap between technology signals and business outcomes.
What Is Business Observability?
Business Observability is the ability to understand, measure, and optimize business performance by correlating technical telemetry (logs, metrics, traces, events) with business KPIs in real time.
Unlike traditional monitoring which focuses on whether systems are “up” or “down”, business observability answers higher-order questions such as
- Why did checkout failures spike during a campaign?
- How does API latency affect customer conversion?
- Which system degradation is impacting revenue, SLAs, or customer experience?
- What technical changes influence churn, fulfillment delays, or compliance risks?
How Business Observability Works?
Business observability works by creating a unified view across three layers
- Technology Signals– Data collected from infrastructure, applications, APIs, microservices, databases, and cloud platforms, logs, metrics, traces, and events.
- Business Context– Mapping telemetry to business workflows, user journeys, transactions, revenue streams, SLAs, and regulatory requirements.
- Intelligent Correlation & Insights– Using analytics, AI, and automation to identify patterns, anomalies, root causes, and business impact, often in real time.
This correlation allows organizations to move from reactive firefighting to proactive, outcome-driven decision-making.
The Business Value of Observability
The true value of observability lies in its ability to connect technology performance with business performance.
Main business outcomes include
- Faster detection and resolution of revenue-impacting issues
- Improved customer experience through consistent performance
- Reduced downtime and operational risk
- Better prioritization of engineering effort
- Higher confidence in digital transformation initiatives
Organizations with strong observability practices don’t just keep systems running, they optimize how systems drive growth.
Components of Business Observability
A mature business observability framework typically includes the following
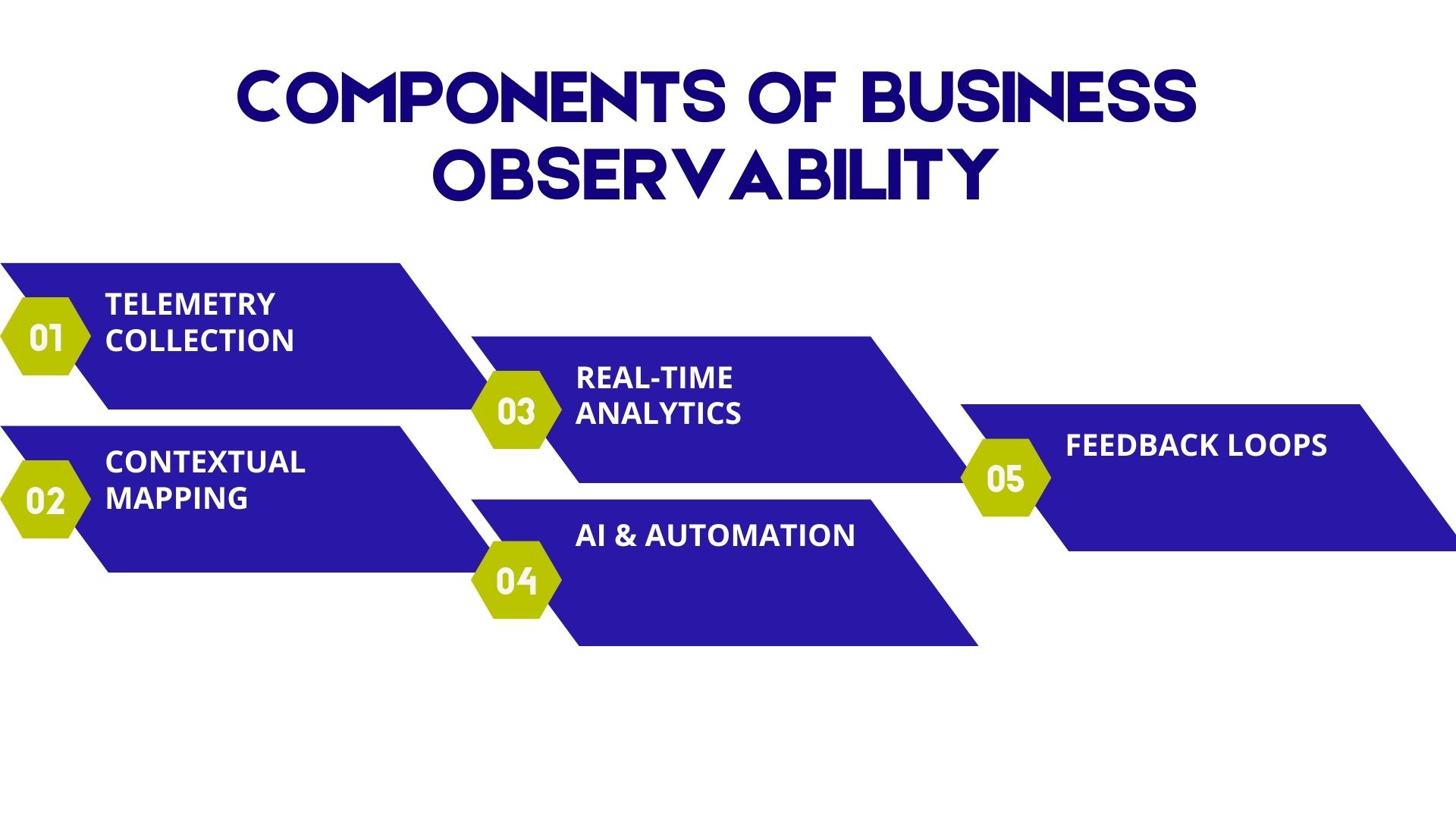
- Telemetry Collection
Logs, metrics, traces, events, and user experience data collected across hybrid and cloud-native environments.
- Contextual Mapping
Linking telemetry to business services, workflows, customers, regions, and revenue streams.
- Real-Time Analytics
Dashboards, alerts, and anomaly detection that highlight both technical and business deviations.
- AI & Automation
Machine learning models that predict failures, identify root causes, and recommend corrective actions.
- Feedback Loops
Continuous learning systems that refine thresholds, correlations, and operational responses over time.
Observability in the Age of AI
As organizations adopt AI and machine learning, observability becomes even more important.
AI systems introduce new complexities like model drift, data quality issues, latency-sensitive inference pipelines, and ethical and compliance risks.
AI observability ensures visibility across
- Data pipelines and feature stores
- Model training and inference performance
- Bias, accuracy, and explainability metrics
- Business outcomes influenced by AI decisions

Observability, Platform Engineering, and Developer Experience
Modern enterprises are increasingly adopting platform engineering to streamline development and operations. Observability is a foundational pillar of this approach.
For Platform Teams
- Provides standardized visibility across teams and services
- Enables self-service diagnostics and faster incident response
- Reduces operational toil through automation
For Developers
- Improves debugging speed and confidence
- Enables understanding of how code impacts real users
- Encourages ownership of outcomes, not just deployments
Strong observability directly enhances Developer Experience (DX), leading to higher productivity, better software quality, and faster innovation.
Business Observability Use Cases
- E-commerce– Correlating cart abandonment with latency, payment failures, or inventory sync issues
- Banking & FinTech– Monitoring transaction success rates against compliance and fraud signals
- Healthcare– Ensuring system reliability across patient journeys and clinical workflows
- Manufacturing– Linking system outages to production delays and supply chain disruptions
- SaaS– Connecting feature performance with user adoption, churn, and ARR
In each case, observability moves beyond IT metrics to business accountability.
Benefits of Business Observability
Organizations that invest in business observability experience
- Faster Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR)
- Reduced operational and financial risk
- Higher customer satisfaction and trust
- Improved cross-team collaboration
- Data-driven prioritization of technology investments
- Greater resilience in complex, distributed systems

Our Commitment to Observability at PCPL
Observability is not an afterthought at PCPL, but it is built into how we design, engineer, and operate systems.
Our commitment includes the following
- Designing observability-first architectures
- Embedding business context into monitoring strategies
- Using AI for intelligent insights and automation
- Enabling platform-led observability for scale
- Empowering teams with actionable, outcome-driven visibility
We help organizations move from knowing what broke to understanding why it matters—and what to do next.
Technology defines competitive advantage in this age and business observability is no longer optional. It is the lens through which organizations can see, understand, and optimize the digital heartbeat of their business.
References
https://www.ibm.com/think/insights/business-observability

